“For my whole life my mom and dad would leave home at 3 a.m. and get back at 7 p.m.,” he says. “They’re always working to make ends meet and always stressed out at the end of the month trying to meet the rent.”
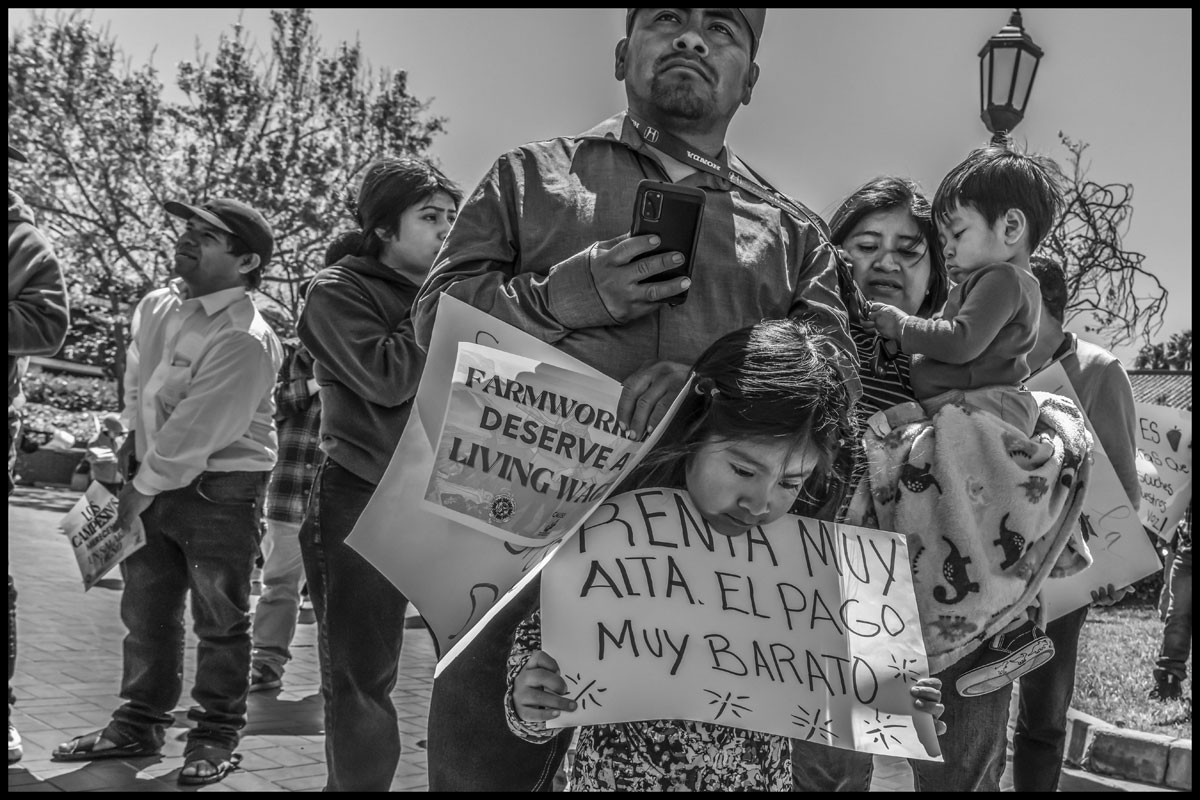

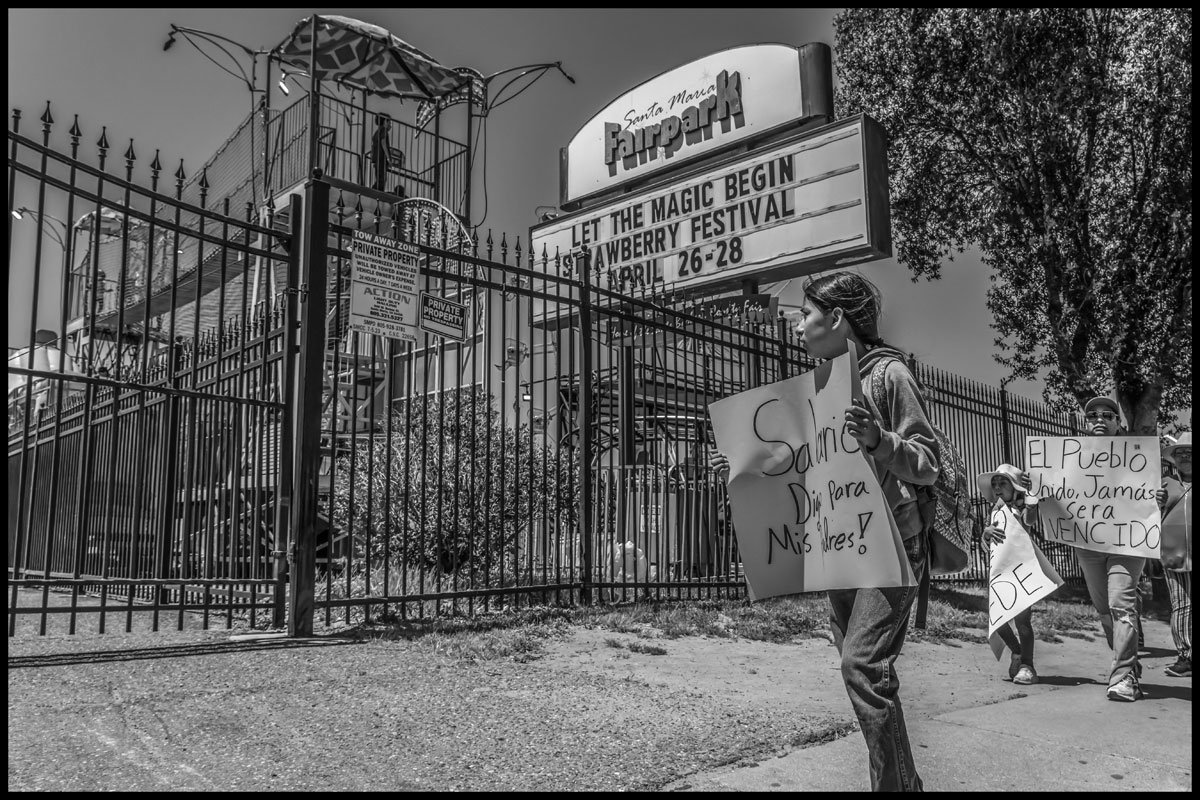
A farmworker family at a 2024 march in Santa Maria, demanding a living wage. One sign reads, “Rent very high. Pay very cheap.”
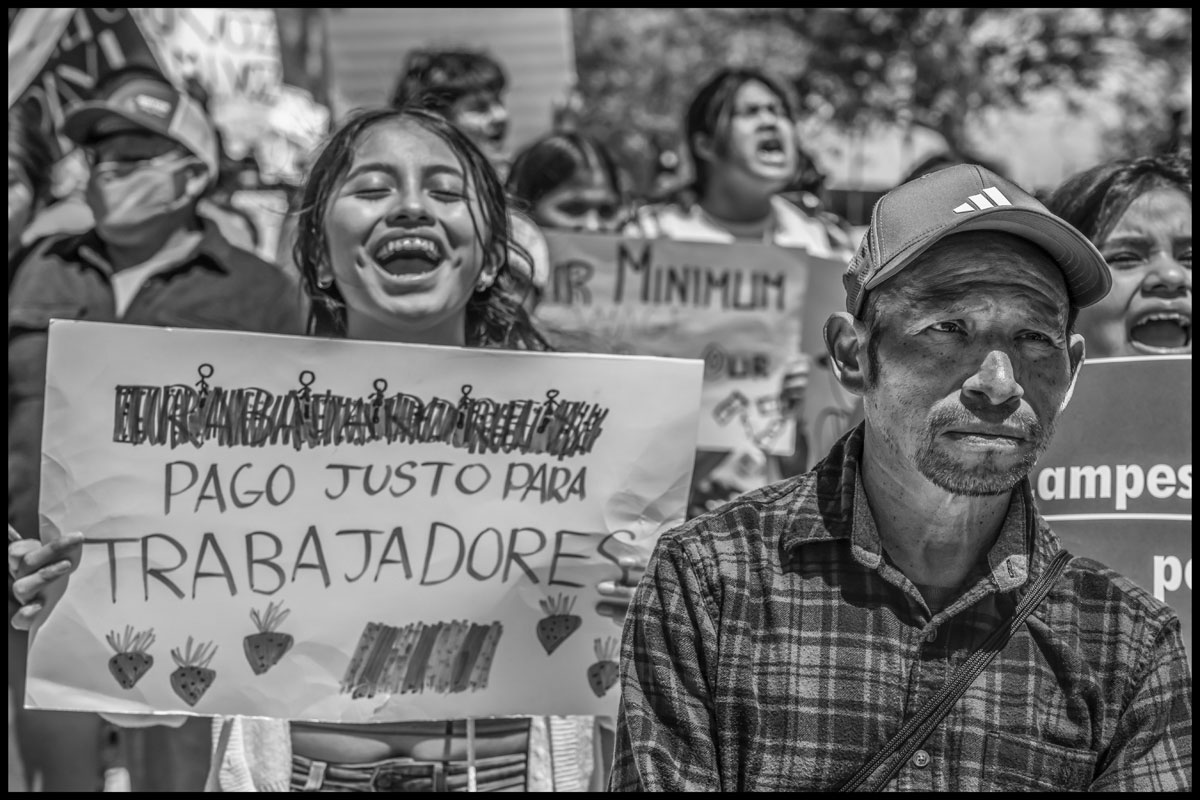
This year, there’s fresh urgency motivating these young protesters: Those long, exhausting workdays are harder to get. “Many of us have no work or only get four or five hours before we’re sent home,” Lozano says. When workers go out to a field to ask a foreman or a labor contractor for a job, he says, they’re often turned away. Increasingly, people fear being displaced from jobs they’ve depended on for years. These longterm, experienced workers are the lifeblood of agriculture in the Santa Maria Valley.
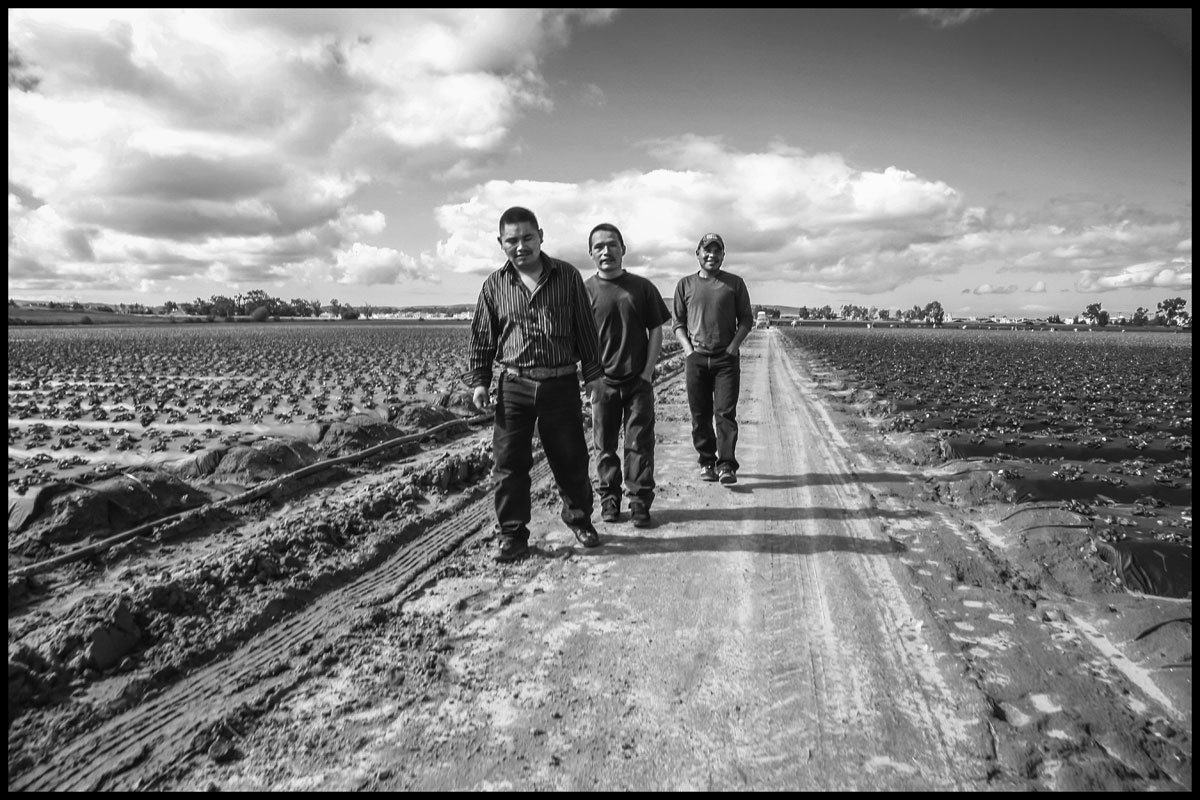

Three farmworkers living in Santa Maria walk out of a field, after having been told by the foreman of a crew picking strawberries that there was no work for them.
At the same time, rents are rising and there are fewer available places to live. Both work and housing pressures, say local labor organizers, can be traced to an important element of the administration’s immigration policy: increasing the numbers of H-2A guest workers.
The Rise in H-2A Workers
The number of seasonal workers recruited from Mexico to labor in Santa Maria Valley fields, on temporary H-2A visas, has been growing every year. That increase is part of a national trend. Twenty years ago, the Department of Labor (DOL) issued 48,336 certifications to growers for workers brought to the United States with H-2A work visas.
In 2017, Trump’s first year in office, growers received 200,049 certifications, and in Biden’s last year, 2024, they received 384,900. The total number of farmworkers in the U.S. is about 2 million, and today, almost a fifth are temporary workers on H-2A visas.
H-2A workers, almost all of whom are young men, are often not treated fairly. They must sign contracts for a maximum of 10 months per year, after which they have to return home, usually to Mexico. They can only work for the grower who recruits them, and can be fired for protesting, organizing, or simply working too slowly.
Fired workers lose their visas and must leave the country and then are usually blacklisted by recruiters. This makes them very vulnerable to pressure and illegal conditions.
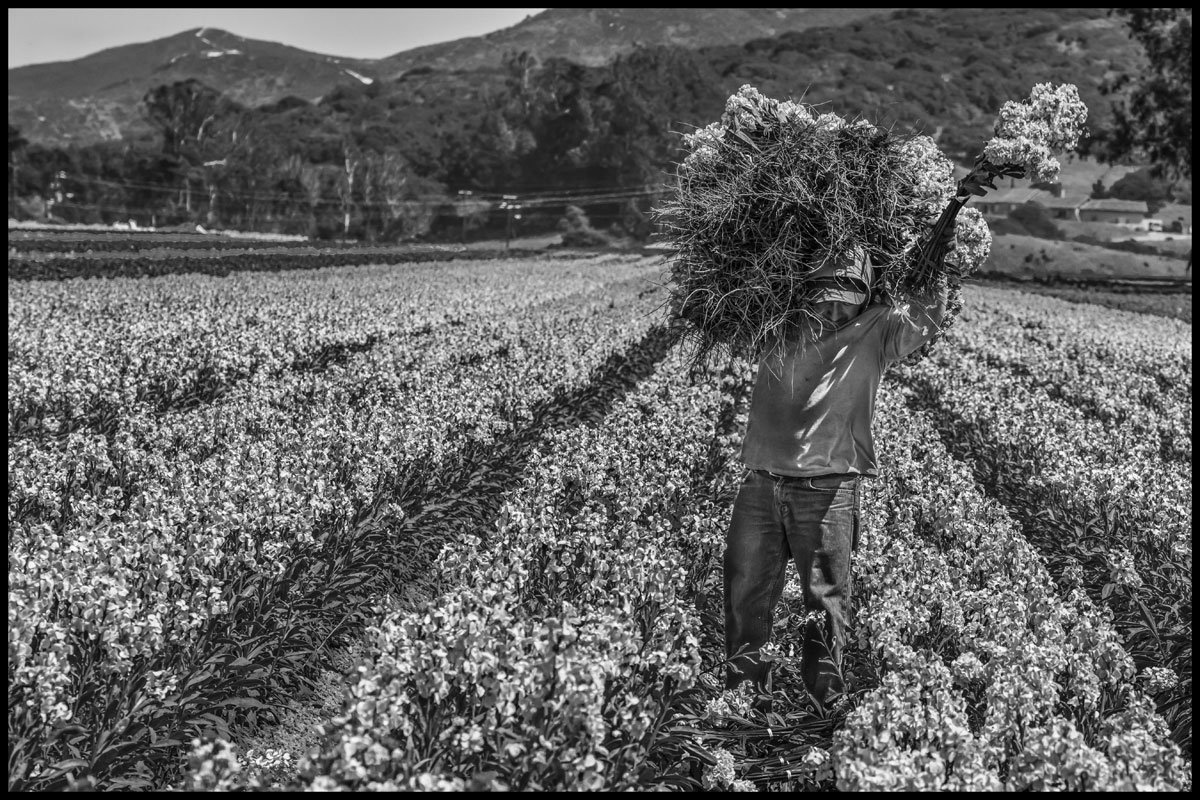

An H-2A worker hoists a load of flowers in a field in Lompoc, near Santa Maria.
In some states, the number of H-2A workers now exceeds the number of local workers. In Florida, with its anti-immigrant and anti-farmworker laws, growers’ 47,416 H-2A certifications last year covered over half of the 80,821 people employed on its farms. Georgia’s 43,436 certifications were for over three-quarters of its 55,990 farm laborers.
In Santa Barbara County, where Santa Maria is located, and in neighboring San Luis Obispo County, the total number of farmworkers is close to 25,000. The Employer Data Hub of the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, which verifies employers’ visa applications for H-2A workers, lists 29 growers and labor contractors employing a total of 8,140 workers, or at least a quarter of all the farmworkers in the two-county area. This is the highest concentration of H-2A workers in California.
The threats from the Trump administration of increased immigration enforcement have been accompanied by movements within farm groups—who strongly backed Trump’s election—to make it easier for growers to use the H-2A system, including by lowering wages and softening housing requirements. In 2020, in Trump’s first term in office, then Agriculture Secretary Sonny Perdue emphasized the government’s support for more H-2A workers. “That’s what agriculture needs, and that’s what we want,” he said at the time.
In her nomination hearing, Trump’s current secretary of agriculture, Brooke Rollins, told Congress that she’d modernize the H-2A program to “make sure that none of these farms or dairy producers are put out of business [by immigration enforcement].”
“There is a growing competition between the new migrants (the H-2A) and the old (the settled Mexican families).”
In his last term, Trump froze the wages of H-2A workers for two years, in effect lowering them because federal regulations would have required increasing them annually. The administration estimated that the move saved growers $170 million each year. In addition, Trump allowed growers to access, for H2-A housing, funds that had been earmarked for year-round farmworker housing.
He also allowed growers to use, for H-2A workers, the federal labor camps started in the 1930s for housing farmworker families at affordable rents financed by USDA.
Impact on Local Workers
In Santa Maria, the increase in H-2A employment is connected to the growth of the strawberry industry. According to a report by Marcos Lopez, a staff member at the U.C. Davis Community and Labor Center, over half of the H-2A certifications in California come from the five counties that are the heart of the state’s strawberry industry, which produces 84 percent of all strawberries in the country.
“The H-2A program grows where the strawberry industry is growing,” Lopez says. While the H-2A wage is higher than the state’s minimum wage ($19.97 per hour versus $16.50), the productivity of H-2A workers is higher because growers recruit young men and then require them to work at a fast rate in order to keep their jobs. This is particularly important in strawberries because it is a highly labor-intensive crop.
As growers bring in the H-2A workers, Santa Maria farmworkers are feeling the impact–in terms of less work, rising rents, and inadequate wages.
Many local Santa Maria farmworkers, themselves immigrants (the majority undocumented) who have been living and working in the valley for years, say they are often sent home after working only four or five hours, and that they can’t get steady work every day. Since they rely on the strawberry season to save enough to get through the leaner months of winter, the loss of hours can reverberate through the rest of the year.
In a study of the social impact of the H-2A program in Salinas, demographer Rick Mines predicted that “the older settled workers will be getting less work as their younger co-nationals [the H-2A] replace them in the fields.” That is how the H-2A program is likely to play out in Santa Maria as well, according to Martinez and others.
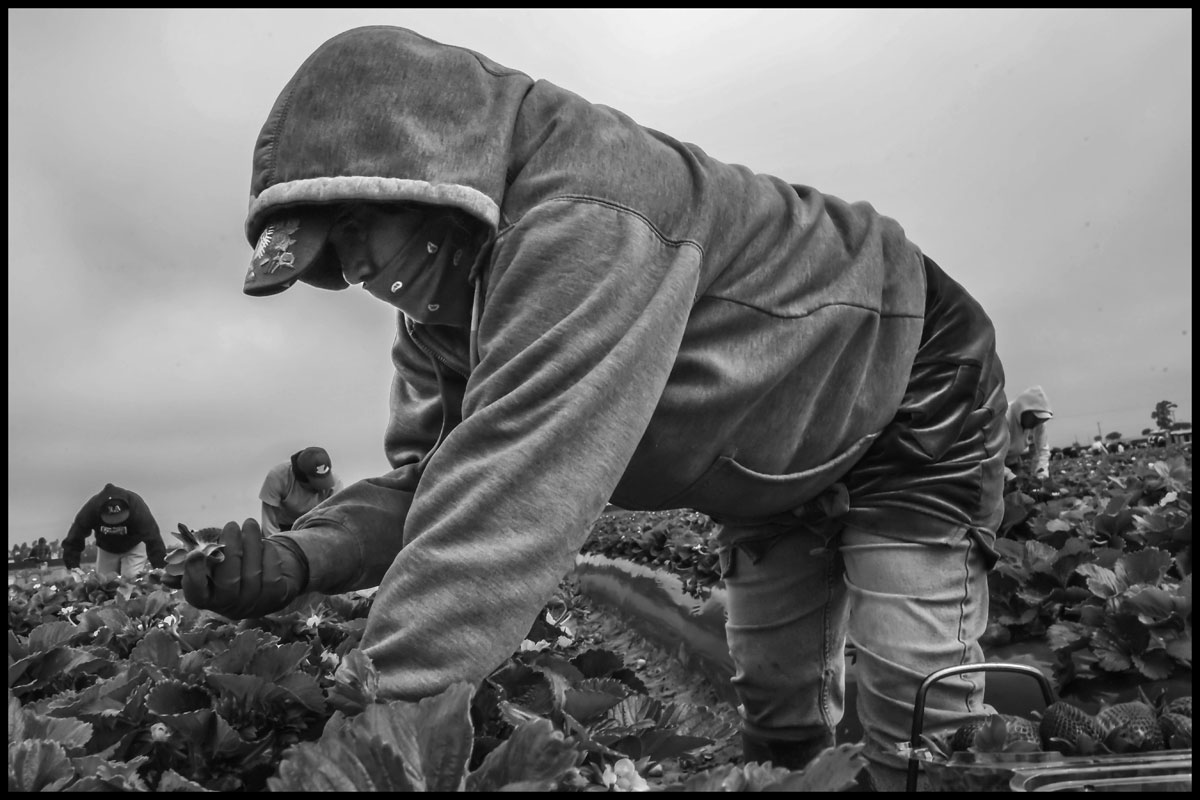

A worker picks strawberries in a field near Santa Maria.
Mines also looked at housing conditions in Salinas. “There is a growing competition between the new migrants [the H-2A] and the old [settled Mexican families]. This competition affects the availability of housing as the older migrants face higher prices and increased crowding in the apartments where most live.”
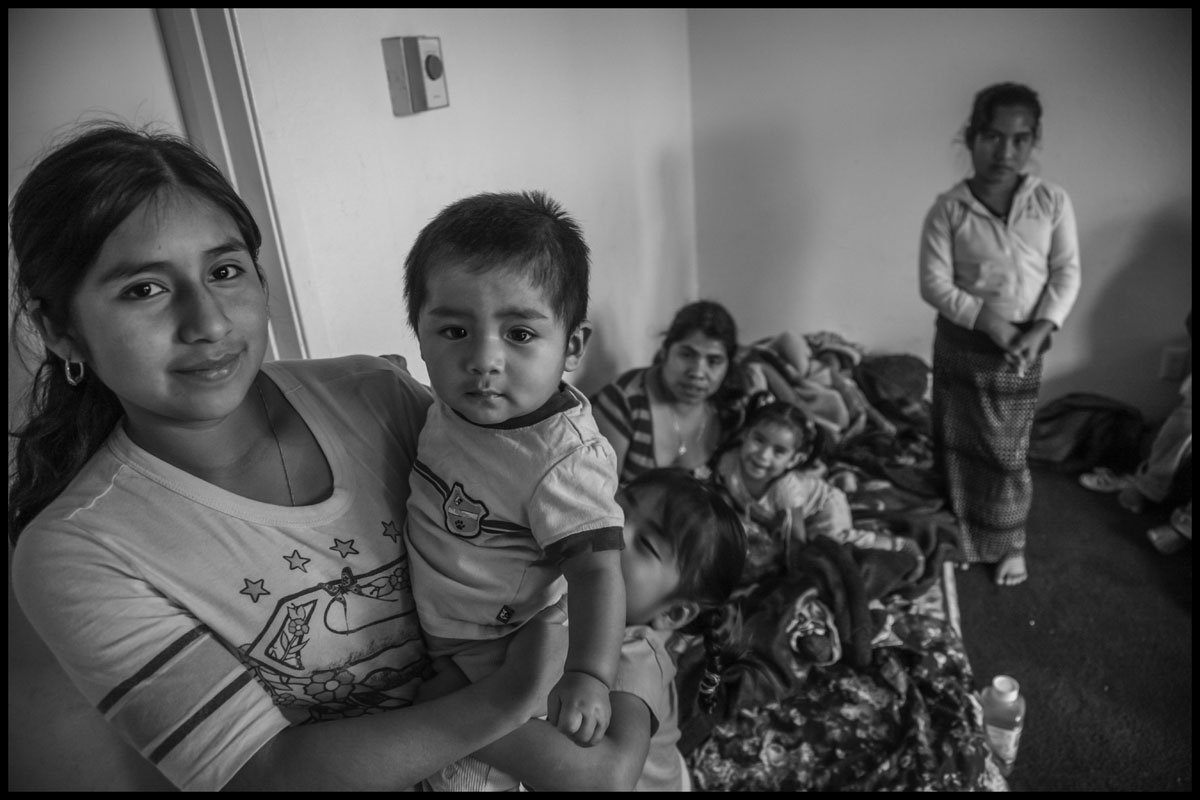

A strawberry picker, her son, and other members of her family sleep in one room in their Santa Maria apartment.
Similar pressures exist in Santa Maria. Growers are obligated to provide housing to H-2A workers, and in Santa Maria, in addition to housing those workers in complexes, the growers also rent houses in working-class neighborhoods. That has led to steep rises in rents, as growers outbid residents for leases.
“I rent my house for $3,000,” explains Francisco Lozano, “but the grower can pay $4,000 or $5,000 and put four people in each bedroom and the living room.”
In 2019, Santa Maria passed an ordinance requiring growers to obtain permits to house H-2A workers in neighborhoods with single-family homes. According to earlier reporting by the Santa Maria Sun, Jason Sharrett, representing the California Strawberry Commission in a city council meeting, called the ordinance unnecessary and “based on erroneous findings.”























Leave a Comment